
 teens have been the target of cyberbullying, with name-calling and rumor-spreading being the most common forms of harassment" width="417" height="517" />
teens have been the target of cyberbullying, with name-calling and rumor-spreading being the most common forms of harassment" width="417" height="517" />
 teens have been the target of cyberbullying, with name-calling and rumor-spreading being the most common forms of harassment" width="417" height="517" />
teens have been the target of cyberbullying, with name-calling and rumor-spreading being the most common forms of harassment" width="417" height="517" />
For the latest survey data on teens and cyberbullying, see “Teens and Cyberbullying 2022.”
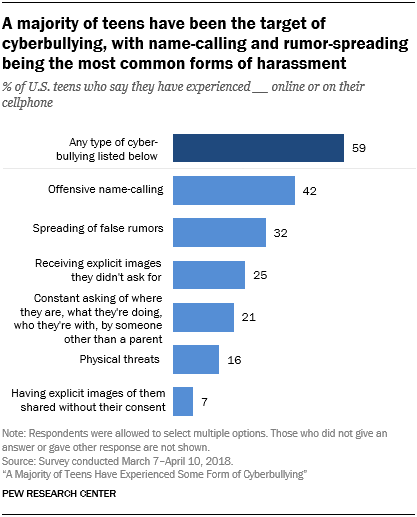
Name-calling and rumor-spreading have long been an unpleasant and challenging aspect of adolescent life. But the proliferation of smartphones and the rise of social media has transformed where, when and how bullying takes place. A new Pew Research Center survey finds that 59% of U.S. teens have personally experienced at least one of six types of abusive online behaviors. 1
The most common type of harassment youth encounter online is name-calling. Some 42% of teens say they have been called offensive names online or via their cellphone. Additionally, about a third (32%) of teens say someone has spread false rumors about them on the internet, while smaller shares have had someone other than a parent constantly ask where they are, who they’re with or what they’re doing (21%) or have been the target of physical threats online (16%).
While texting and digital messaging are a central way teens build and maintain relationships, this level of connectivity may lead to potentially troubling and nonconsensual exchanges. One-quarter of teens say they have been sent explicit images they didn’t ask for, while 7% say someone has shared explicit images of them without their consent. These experiences are particularly concerning to parents. Fully 57% of parents of teens say they worry about their teen receiving or sending explicit images, including about one-quarter who say this worries them a lot, according to a separate Center survey of parents.
The vast majority of teens (90% in this case) believe online harassment is a problem that affects people their age, and 63% say this is a major problem. But majorities of young people think key groups, such as teachers, social media companies and politicians are failing at tackling this issue. By contrast, teens have a more positive assessment of the way parents are addressing cyberbullying.
These are some of the key findings from the Center’s surveys of 743 teens and 1,058 parents living in the U.S. conducted March 7 to April 10, 2018. Throughout the report, “teens” refers to those ages 13 to 17, and “parents of teens” are those who are the parent or guardian of someone in that age range.
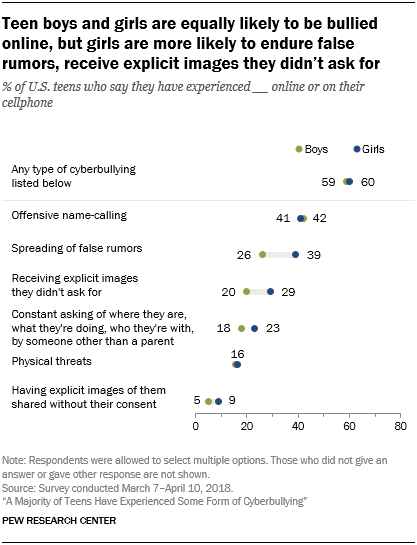
When it comes to the overall findings on the six experiences measured in this survey, teenage boys and girls are equally likely to experience cyberbullying. However, there are some differences in the specific types of harassment they encounter.
Overall, 60% of girls and 59% of boys have experienced at least one of six abusive online behaviors. While similar shares of boys and girls have encountered abuse, such as name-calling or physical threats online, other forms of cyberbullying are more prevalent among girls. Some 39% of girls say someone has spread false rumors about them online, compared with 26% of boys who say this.
Girls also are more likely than boys to report being the recipient of explicit images they did not ask for (29% vs. 20%). And being the target of these types of messages is an especially common experience for older girls: 35% of girls ages 15 to 17 say they have received unwanted explicit images, compared with about one-in-five boys in this age range and younger teens of both genders. 2
Online harassment does not necessarily begin and end with one specific behavior, and 40% of teens have experienced two or more of these actions. Girls are more likely than boys to have experienced several different forms of online bullying, however. Some 15% of teen girls have been the target of at least four of these online behaviors, compared with 6% of boys.
In addition to these gender differences, teens from lower-income families are more likely than those from higher-income families to encounter certain forms of online bullying. For example, 24% of teens whose household income is less than $30,000 a year say they have been the target of physical threats online, compared with 12% whose annual household income is $75,000 or more. However, teens’ experiences with these issues do not statistically differ by race or ethnicity, or by their parent’s level of educational attainment. (For details on experiences with online bullying by different demographic groups, see Appendix A.)
The likelihood of teens facing abusive behavior also varies by how often teens go online. Some 45% of teens say they are online almost constantly, and these constant users are more likely to face online harassment. Fully 67% of teens who are online almost constantly have been cyberbullied, compared with 53% of those who use the internet several times a day or less. These differences also extend to specific kinds of behaviors. For example, half of teens who are near-constant internet users say they have been called offensive names online, compared with about a third (36%) who use the internet less frequently.
Today, school officials, tech companies and lawmakers are looking for ways to combat cyberbullying. Some schools have implemented policies that punish students for harassing messages even when those exchanges occur off campus. Anti-bullying tools are being rolled out by social media companies, and several states have enacted laws prohibiting cyberbullying and other forms of electronic harassment. In light of these efforts, Pew Research Center asked young people to rate how key groups are responding to cyberbullying and found that teens generally are critical of the way this problem is being addressed.
 teens think parents are doing a good job in addressing online harassment, but are critical of teachers, social media companies and politicians" width="417" height="434" />
teens think parents are doing a good job in addressing online harassment, but are critical of teachers, social media companies and politicians" width="417" height="434" />
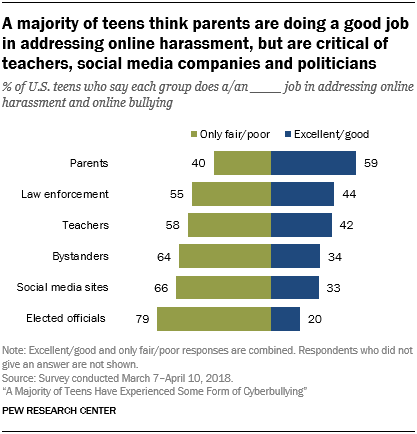
Indeed, teens rate the anti-bullying efforts of five of the six groups measured in the survey more negatively than positively. Parents are the only group for which a majority of teens (59%) express a favorable view of their efforts.
Young people have an especially negative view of the way politicians are tackling the issue of cyberbullying – 79% of teens say elected officials are doing only a fair or poor job of addressing this problem. And smaller majorities have unfavorable views of how groups such as social media sites (66%), other users who witness harassment happening online (64%) or teachers (58%) are addressing harassment and cyberbullying.
Teens’ views on how well each of these groups is handling this issue vary little by their own personal experiences with cyberbullying – that is, bullied teens are no more critical than their non-bullied peers. And teens across various demographic groups tend to have a similar assessment of how these groups are addressing online harassment.
Parents believe they can provide their teen with the appropriate advice to make good online decisions. Nine-in-ten parents say they are at least somewhat confident they can teach their teen how to engage in appropriate online behavior, including 45% who say they are very confident in their ability to do so.
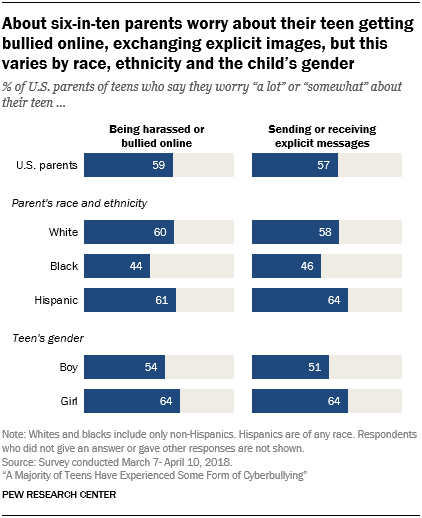
But even as most parents are confident they can educate their child about proper online conduct, notable shares are concerned about the types of negative experiences their teen might encounter online. Roughly six-in-ten parents say they worry at least somewhat about their teen being harassed or bullied online (59%) or sending or receiving explicit images (57%). In each case, about one-in-four parents say they worry a lot about one of these things happening to their child.
These parental concerns tend to vary by race and ethnicity, as well as by a child’s gender. Among parents, whites and Hispanics are more likely than blacks to say they worry about their teen being cyberbullied. Hispanic parents also are more inclined than black parents to say they worry about their child exchanging explicit images. At the same time, parents of teen girls are somewhat more likely than those with a teenage boy to say they worry about their teen being bullied online (64% vs. 54%) or exchanging explicit images (64% vs. 51%). (For details on these parental concerns by demographic group, see Appendix A.)